OSE Derivatives
Platinum Futures, An Important Trading Tool for Building Sustainable Society

Osaka Exchange (OSE) is currently promoting Platinum Futures as part of its efforts to expand Japanese derivative markets. Below, we highlight important features of platinum as a precious metal and identify trading opportunities on Japan’s Platinum Futures market.
About Platinum
Platinum’s most significant characteristic as a precious metal is its rarity. Only about 5,000 tons of platinum has been ever produced, less than one-thirtieth of the 170,000 tons of gold produced.
Platinum is highly prized for both industrial and precious metal uses, unlike gold, for which jewelry makes up over 50% of demand. Due to its high melting point, high density, ultra-stability, and extreme non-corrosiveness, platinum is used in a variety of industries, from the automotive to industrial applications in chemicals, electronics, glass, oil refining and high-temperature measurement, as well as medical and environmental fields. Automotive and industrial uses make up over 70% of platinum demand.
Platinum is found at very low concentration in the earth’s crust compared to gold and silver. Platinum extraction from mining is concentrated in only three areas, with over 70% of global mine supply coming from a relatively small geographic region in South Africa.
Platinum Demand and Supply, 2023 (forecast)
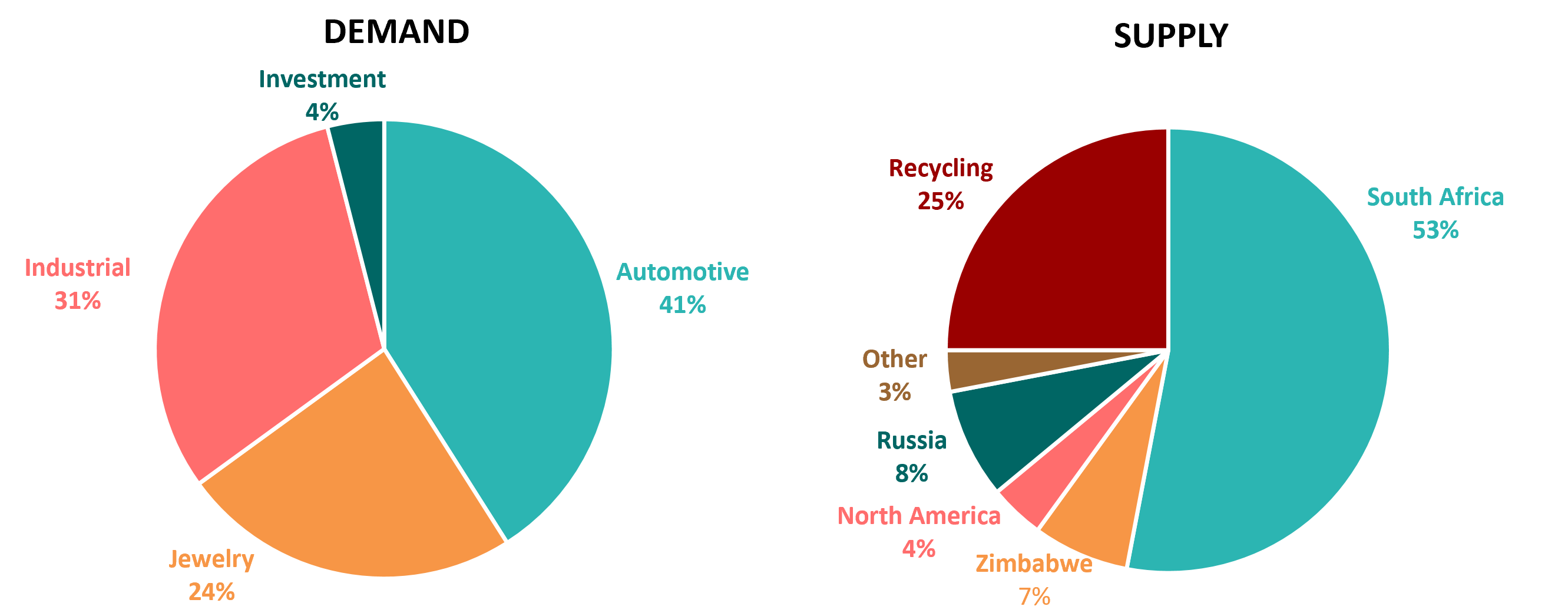
Though scarce, demand for platinum is highly variable based on its use in a variety of industries. In fact, the market for platinum is demand-driven, owing to platinum’s unique combination of physical and chemical properties and a diversity of applications. This supply/demand environment of platinum presents both significant trading opportunities for traders and growing necessity for hedges against price volatility among industrial and business users.
For more information on platinum as a precious metal, including demand, supply, and the investment environment, see the article written by the World Platinum Investment Council.
Overview of Japan’s Platinum Futures
Platinum futures trading in Japan began in 1984. Shortly thereafter, the Japanese market was the most heavily traded platinum futures market in the world until it was overtaken by the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYMEX) in the 2000s. The large demand for physical platinum in Japan, the strong preference for platinum as a precious metal among Japanese people, and the high volatility of the futures price made it an attractive investment for many retail investors.
As of 2023, platinum futures traded on OSE are second only to NYMEX in terms of markets opened to global investors. In annual trading volume for 2022, OSE counted 2.5 million platinum futures contracts compared to 5.4 million on NYMEX.
In order to meet diversifying investment demands in Japan and overseas, OSE opened a Platinum Mini Futures (1/10th standard contract size) market in 2008 and a Platinum Rolling-Spot Futures market in 2017.
Platinum-related Derivatives Traded on OSE
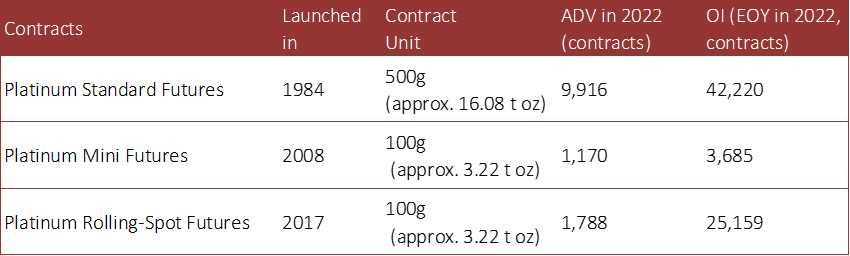
A significant feature of OSE’s platinum futures contract is its small in size and contract unit expressed in grams.
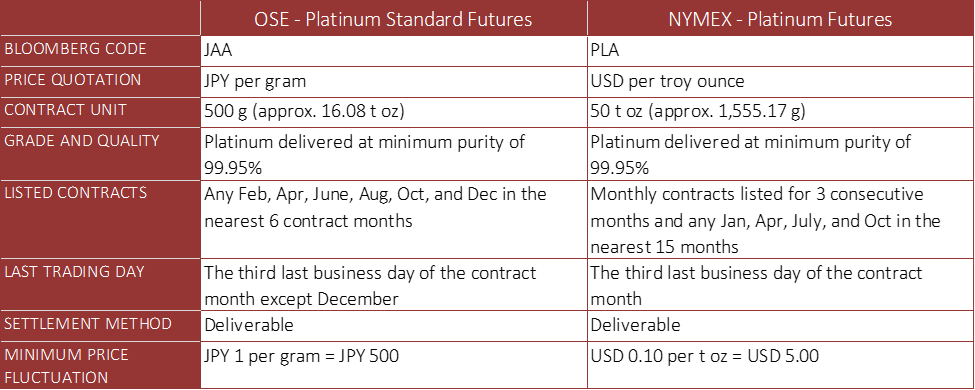
For example, the contract unit for OSE Platinum Standard Futures is 500 g (approx. 16.08 t oz), while the contract unit for NYMEX Platinum futures is 50 t oz (approx. 1,555 g). OSE’s trading unit is about one-thirds of NYMEX’s unit, but slightly larger than the NYMEX Micro Platinum Futures (10 t oz, approx. 311 g), which began trading in March 2023. OSE’s smaller contract unit was designed with domestic retail investors in mind, as they have historically been primary traders of platinum futures.
Like OSE Gold futures, the OSE Platinum futures contract is denominated in Japanese yen, and the Platinum Standard Futures, which are the most liquid, are settled on a delivery basis.
Platinum Futures on OSE vs NYMEX
It is important to note that the most liquid contract month for OSE platinum futures is the 6th contract month. This is common to all commodity futures traded in Japan and is a holdover from when the main traders were domestic retail investors.
Trading Volume by Contract Month, Share of Open Interest Outstanding (March, 2023)
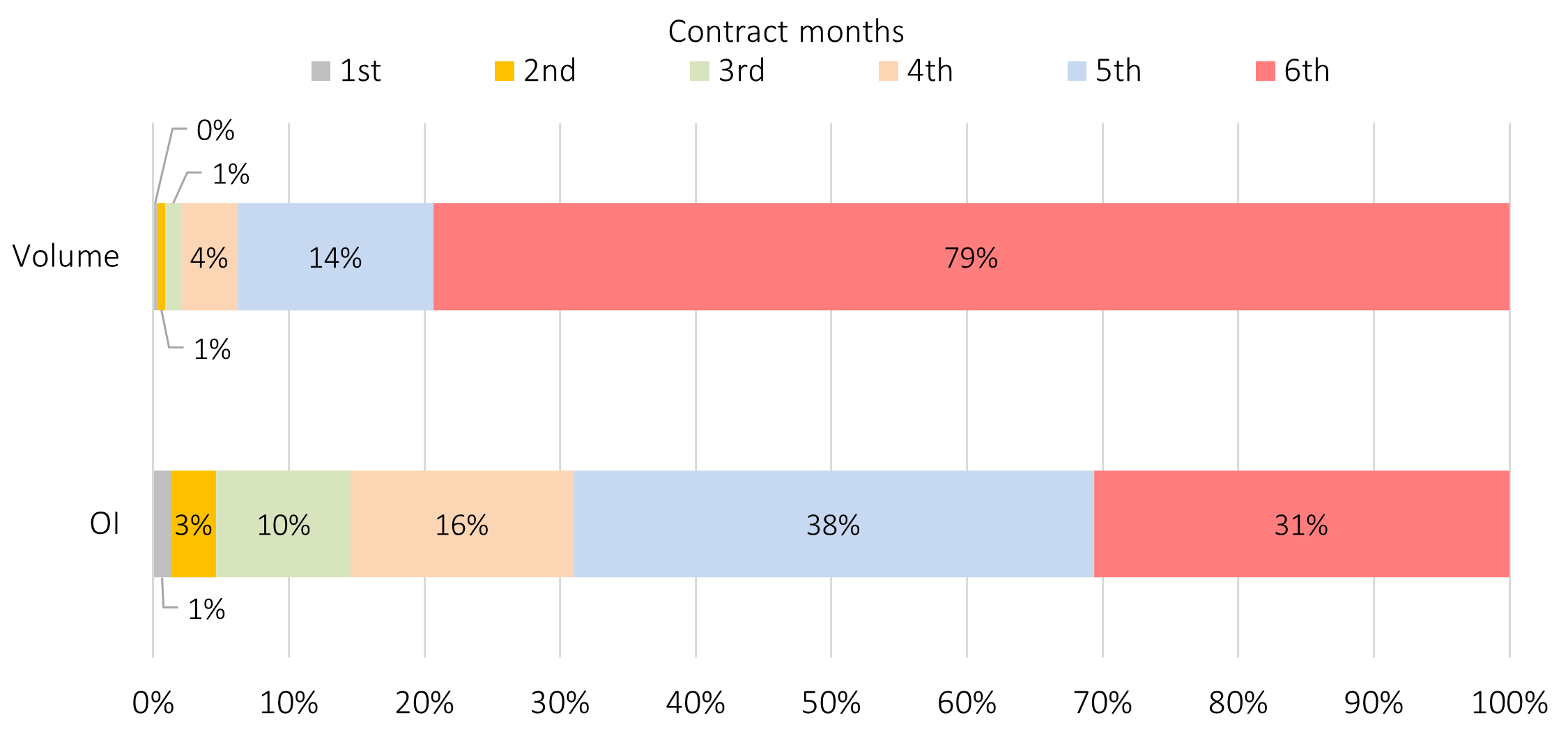
For details, see the OSE platinum futures contract specifications.
Market Trend of Japan’s Platinum Futures
Platinum futures traded on OSE claim the second highest market liquidity among the precious metals futures category after gold futures. In 2022, Average Daily Volume (ADV) and Open Interest (OI) for Platinum Standard Futures were 10,336 contracts and 32,427 contracts, respectively, while ADV and OI for Gold Standard Futures were 30,232 contracts and 44,397 contracts, respectively.
Monthly Average Daily Volume (ADV) & Open Interest (OI) of Platinum Standard Futures
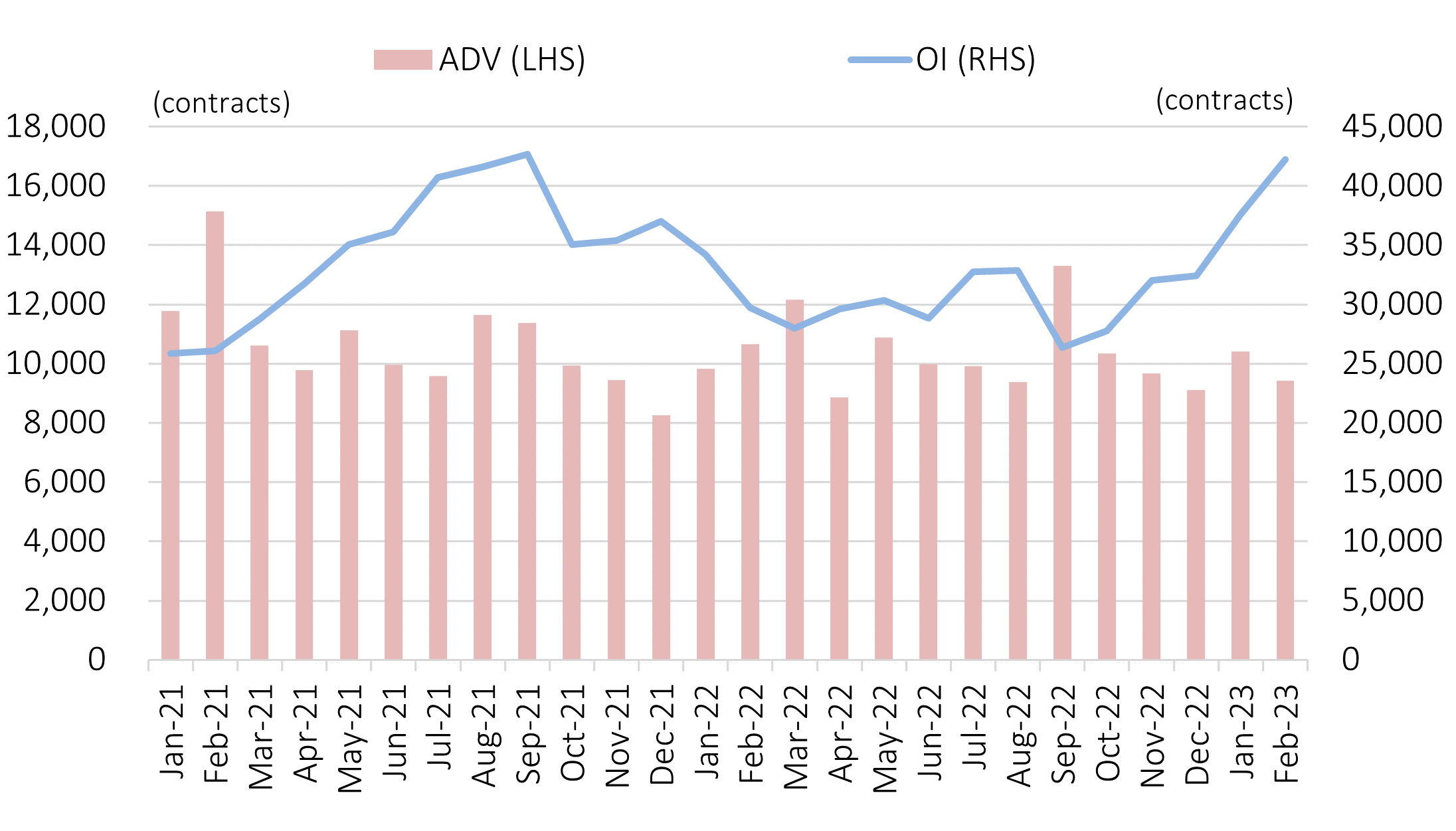
Source: JPX
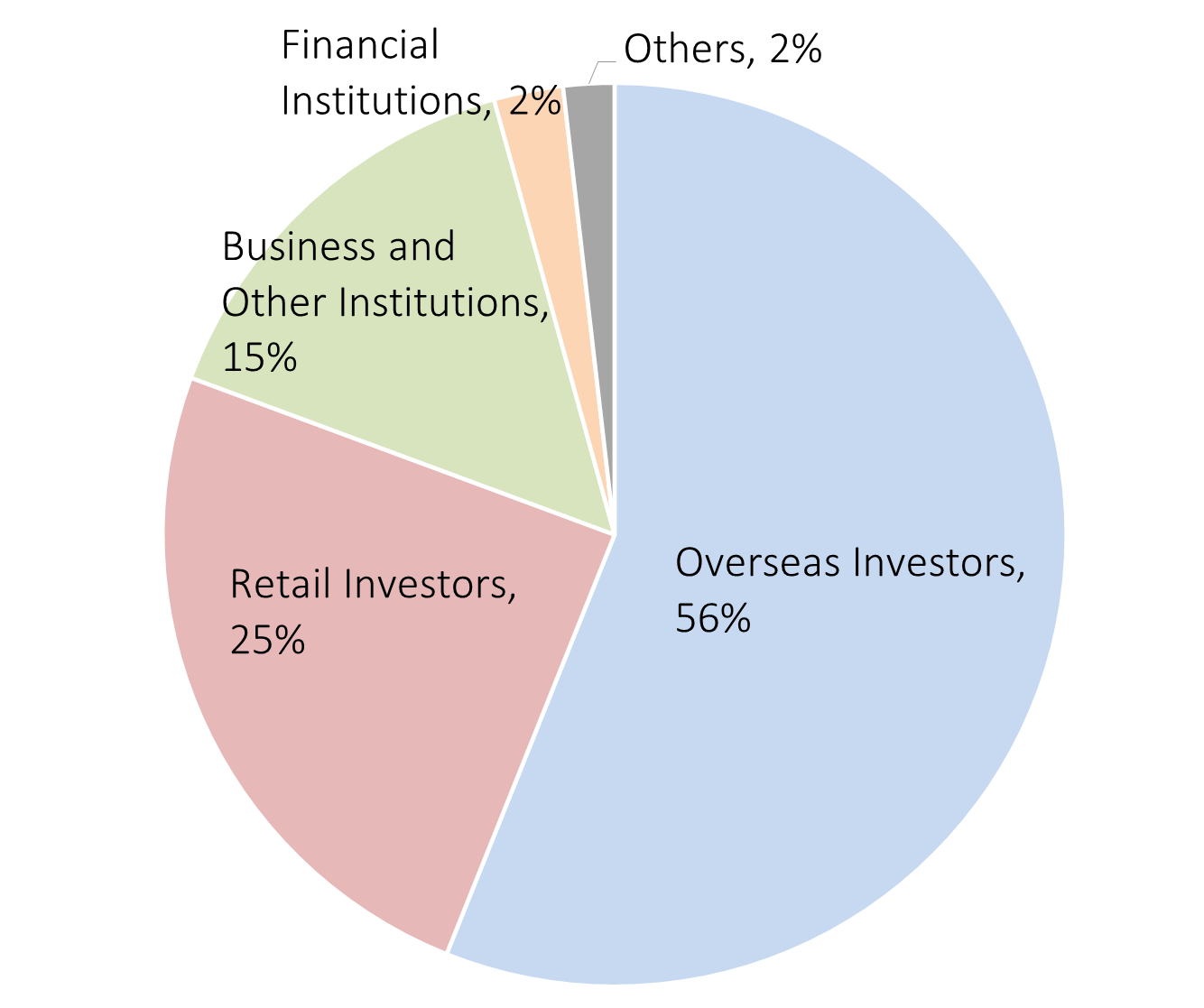
Overseas investors comprise the largest share of trading volume in OSE Platinum Standard Futures at 56%, followed by domestic retail investors at 25%. In OSE Gold Standard Futures, overseas investors make up 68% of the market share and domestic retail investors make up 21%. Retail investors’ share in the Nikkei 225 mini, the most actively traded futures by retail investors, is 23%, so a 25% share in Platinum Futures looks quite high.
Trading in Platinum Standard Futures by Investors Type in 2022
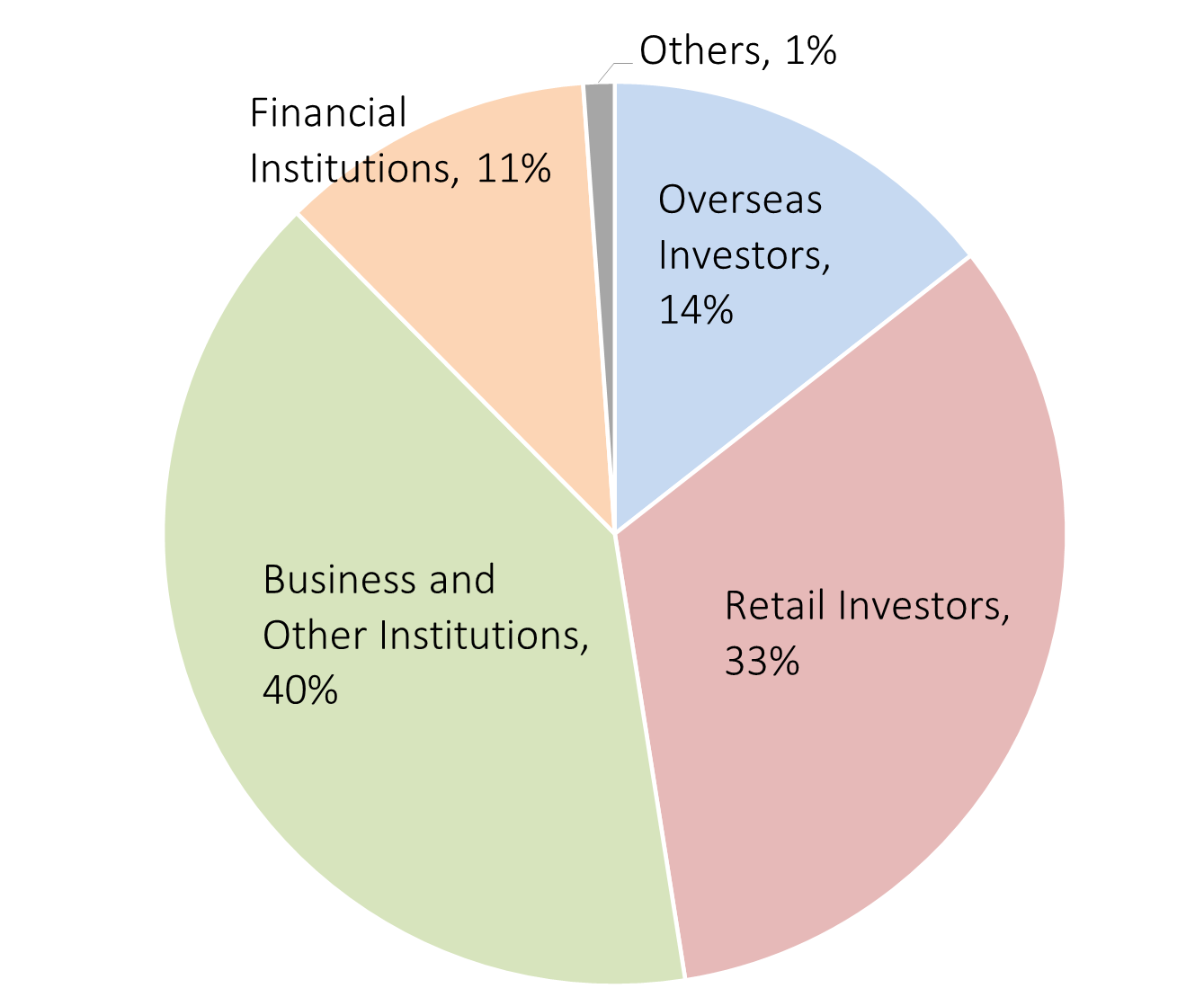
Open Interest, which indicates contract holders and their positions, shows overseas investors, who used to account for half of the trading volume, now hold 14% of the positions, while commercial players and retail investors have a larger share. This suggests that overseas investors are mainly dominated by traders that don’t carry over their positions, such as HFTs (high frequency trading) and daily dealers.
Holding Positions in Platinum Standard Futures by Investors Type, 2022
As stated above, the final settlement method for Platinum Standard Futures is physical delivery, and the delivery amount for 2022 was 2,465 contracts, approximately 8% of the OI balance of 32,427 contracts at the end of 2022. This is higher than the approximately 5% of Gold Standard Futures, and is thought to reflect platinum’s utility as an industrial commodity as well as for jewelry and investments.
The delivery of Platinum Futures is made via warehouse receipts, and the outstanding balance of warehouse receipts issued by OSE-designated warehouses can be found here.
Arbitrage Opportunities with Overseas Markets
Platinum Futures in Japan is an actively traded market, and as such, arbitrage opportunities with overseas markets exist. In fact, many global players are making these trades.
The chart below shows the price movements between OSE and NYMEX Platinum Futures. Given the difference in trading units (grams vs. troy ounces), the price movement of OSE Platinum Futures in the chart below is converted to troy ounces and denominated in USD. Note that taxes, commissions, differences in delivery offerings are not taken into account.
Settlement Prices between OSE and NYMEX in USD
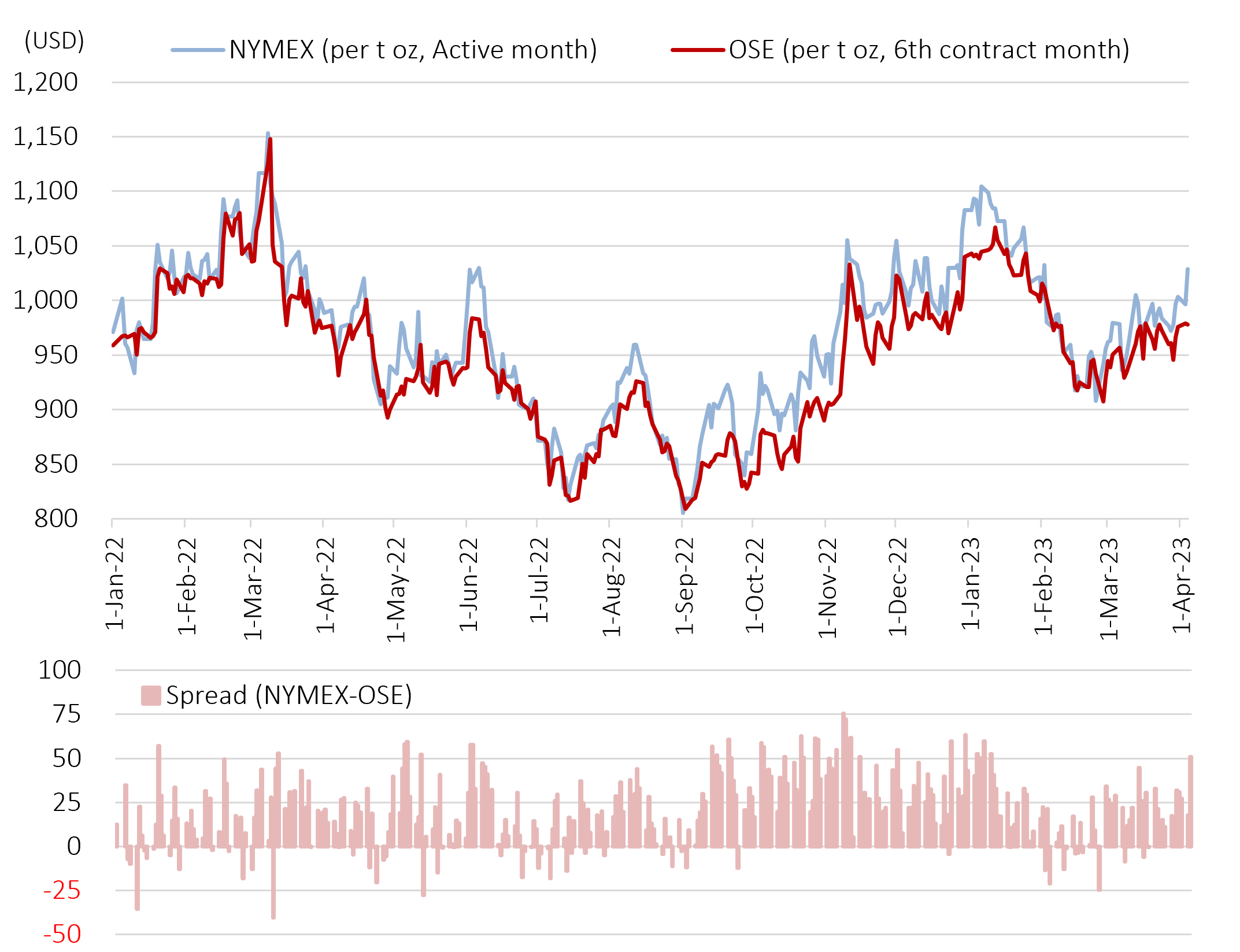
Although OSE Platinum Futures tend to be discounted compared to NYMEX futures, the spread levels are constantly fluctuating due to supply and demand conditions in each market, creating opportunities for inter-market arbitrage trading.
Platinum, a Trading Tool to Achieve a Sustainable Society
Demand for platinum is expected to rise in the future as part of efforts to pursue a sustainable society. Over the next decade, growth in demand will be driven by higher platinum content in catalytic converters as a substitution for more costly palladium as well as to meet tighter emissions standards; loading as a catalyst in fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs); and uses in the production of green hydrogen.
In this context, platinum futures will play an important role as a price hedging tool, but it is also important that platinum futures themselves take sustainability into account.
As part of this commitment to sustainability, OSE’s Platinum Futures delivery offerings follow OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Supply Chains of Minerals from Conflict-Affected and High-Risk Areas, and OSE will ensure that due diligence is appropriately carried out in supply chains for certain products as needed.
As platinum’s importance in a green society continues to grow, OSE’s Platinum Futures will continue to attract a large global and local investor base due to the size of the market and its investor base.
Related links