OSE Derivatives
Automotive and tyre sectors likely to grow in 2024 but rubber lags due to oversupplied market

Highlights
- Low price environment for physical rubber likely contributed to higher margins for tyre manufacturers in 2023
- Thailand and Ivory Coast emerging as new supply nodes based on trade flows
- Toyota worldwide sales in 2023 exceed pre pandemic levels in 2019 over most months
- The outlook from major financial institutions ranges from flat to moderate growth in 2024
Low price environment for physical rubber likely contributed to better margins for tyre manufacturers in 2023
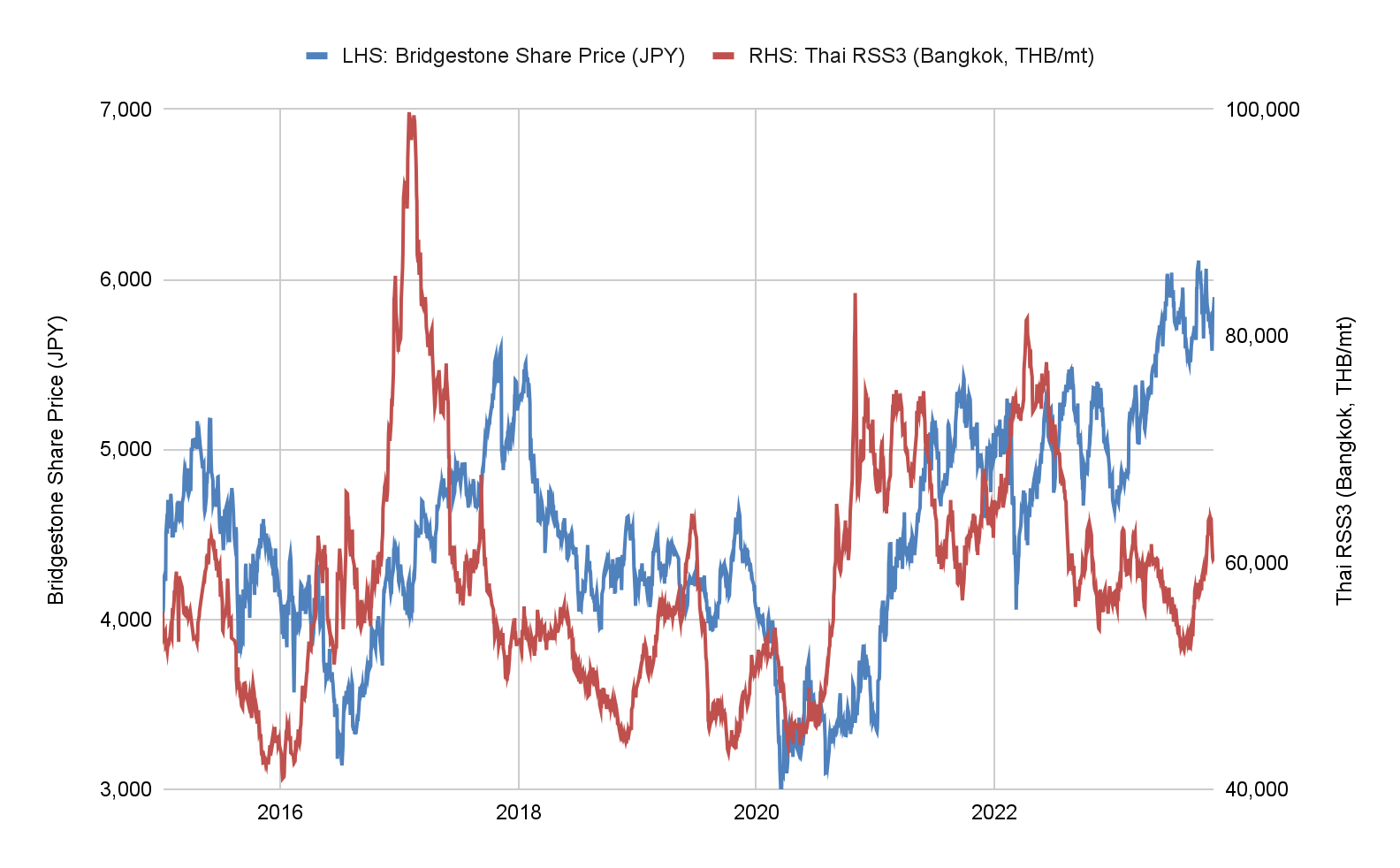
The above chart plots the daily closing price for Bridgestone shares on the left axis, against daily offer prices for Thai Ribbed Smoked Sheets of grade 3 (RSS3) in the physical rubber market from 2015 till early November 2023. This year thus far, prices in physical rubber have been on a declining trend while tyre makers’ shares have risen. As of early November 2023, Bridgestone shares recorded an increase of about 27% with an upward price trend over the year. Physical rubber market RSS3 prices trended to a Year-to-date low in late August 2023, before registering an increase after the Chinese measures to bolster its stock market and economy were announced the same month.
Online research suggests natural rubber accounts for between 25% and 35% of a tyre’s raw material costs. RSS3 is mainly used in the production of heavy vehicle categories such as trucks, buses and aeroplanes. These categories also tend to use a higher proportion of natural rubber than smaller passenger vehicles. The average price for Thai RSS3 since 2015 was about THB 58,608/mt, and was observed higher than average at around THB 60,540/mt in early November 2023. The corresponding prices in USD for both periods were US$1,762/mt since 2015 and US$1,664/mt in early November 2023. Assuming demand stays similar or improves from last year, the downward rubber price trend earlier in the year likely contributed to better profit margins for tyre producers around the globe.
In this example, Bridgestone is used because it represents the largest tyre producer by market share based in Japan and gives good implications for the industry. 1H data for fiscal 2023 also indicates revenue increasing 11% compared to 1H 2022 . If physical rubber prices remain in a low price environment, tyre makers could see higher margins due to low raw material costs. As highlighted in financial results for 1H 2023, a weaker Yen was also one of the factors contributing to higher revenues as most international deals are likely done in US Dollars. However, it is important to note that other factors can influence their cost-revenue structure and share prices.
Thailand and Ivory Coast emerging as new supply nodes based on trade flows
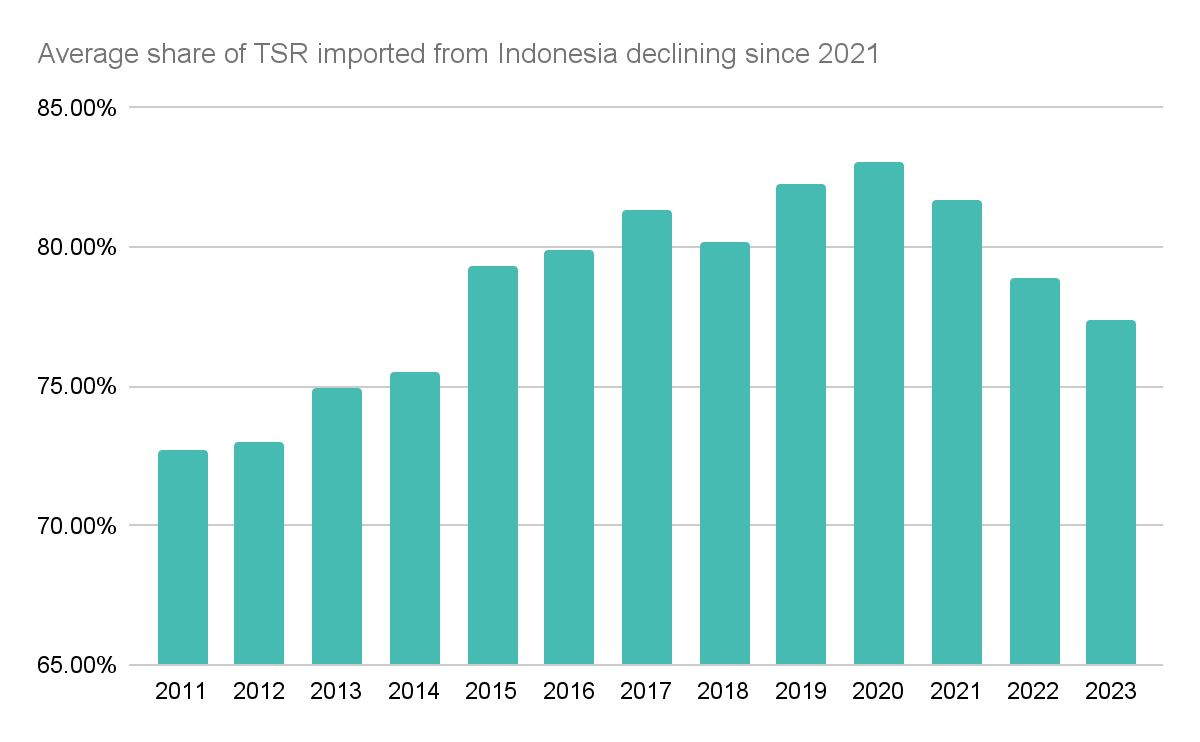
For tyre production, Japanese tyre manufacturers tend to import Indonesian Technically Specified Rubber of grade 20 (SIR20). Since 2011, Japan imported between 24,000 tons and 68,000 tons of TSR monthly, with 60% to 90% originating from Indonesia. Trade statistics show that the import share from Indonesia has been decreasing since 2021, indicating some trade flows diverted to Thailand in recent years.
Over the past few years, Africa has emerged as a major production node for natural rubber. Data shows that Japan imported little TSR from the Ivory Coast, totalling 104 metric tons since 2011. Prior to 2023, only 12 tons were imported while the remainder was imported this year from August till October. This suggests that a new trade flow may have emerged with TSR imported from the Ivory Coast. Importing from these two countries may be a strategy from manufacturers to diversify their supply chain. This may become increasingly important especially as factories based in Indonesia were heard running between 30% to 40% of capacity this year.
Toyota worldwide sales in 2023 exceed pre pandemic levels in 2019 over most months

In the above chart, Toyota is used as a proxy for automotive demand as the largest car manufacturer globally. For the first 9 months in 2023, the number of vehicles sold worldwide posted a YoY increase over 2022 for all months except for January. Comparing 2023 to pre-pandemic levels in 2019, worldwide sales up till September this year have exceeded these levels in 7 out of 9 months. Share prices also showed a rising trend corresponding with the increase in sales worldwide.
In particular, Japanese automakers are expected to perform better than counterparts in the United States. Automobile workers have been on a labour strike from mid-September to end-October 2023. This cost one of the automakers, Ford, the production of about 80,000 units or an impact of about US$100 million on Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT) . Japanese exports into the US are largely unaffected by such strikes, and an increase in production volumes would lead to increasing demand for tyres and subsequently for natural rubber.
The outlook from major financial institutions ranges from flat to moderate growth in 2024
Based on the World Economic Outlook report for October 2023, China’s property sector crisis was also cited as a major risk factor for commodity exporters who are heavily reliant on exports . As of 2022, China accounts for about 40% of global natural rubber demand. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasts nominal GDP to continue growing between 4.9% to 5.3% over the next 5 years. Nominal growth figures are used instead of real growth because shares and RSS3 among other commodities are priced without adjusting for inflation.
The United States Federal Reserve (Fed) projection in September 2023 indicated real GDP growth will slow next year to 1.5% from 2.1% . Contrary to some expectations of a recession in the US last year, the projections have been revised towards an economic expansion for 2023 instead. In November 2023, the Committee voted in favour of maintaining key interest rates between 525 and 550 basis points. Following the vote, key interest rates have been held steady for the past 3 meetings. Market expectations suggest that the Fed will hold rates steady into 2024. In September 2023, the US was the largest export destination with about 34% of motor vehicle exports from Japan.
The European Central bank in September 2023 forecast real GDP to grow at 1% in 2024, representing a 0.3% increase from this year . Demand is expected to continue being low, with the economy in stagnation in the near term before picking up from 2024. As of September 2023, the EU accounted for about 10% of Japanese motor vehicle exports.
The Bank of Japan (BOJ) outlook for economic activity and prices in October 2023 indicate the economy will likely continue to recover at a moderate pace with real GDP growing between 0.9% to 1.4% in 2024. The central bank is expected to maintain expansionary low interest rate policies heading into 2024.
Conclusion: Automotive and tyre sectors likely to grow in 2024 but rubber lags due to oversupplied market
As of September 2023, domestic sales account for about 16% of the total sales made by Toyota. As such, Japanese automakers likely have significant exposure to export demand. For 2024, the IMF and central banks are forecasting slowed growth which may dent demand growth from key markets such as the US. Despite the slower rate of growth, the upward trend in export demand is evident and will likely rise next year.
FY2023 (April 2023 – March 2024) forecasts for Bridgestone also expect demand for the Original Equipment (OE) segment to grow across different regions. This implies that on the whole, tyre demand from automakers has risen in 2023. Demand for the following quarters would still need to be higher year-over-year based on the forecasts. For other manufacturers such as Michelin, growth in the OE segment was also highlighted to be robust. However, weaker replacement tyre demand may cause full-year volumes to be slightly lower.
Although demand for tyres and motor vehicles has grown along with positive GDP growth in 2023, global rubber prices experienced a slump for the majority of the year. The recent price support across physical rubber grades is thought to be driven mainly by Chinese stock market revival measures unveiled in August, rather than an improvement in actual market fundamentals.
Production and consumption data for natural rubber implies the market has been oversupplied since 2012. This oversupply in the form of warehouse inventories globally needs to be cleared before any demand-driven push could drive physical rubber prices toward historical highs of more than US$6,000/mt. In the short-term, the physical rubber market is anticipated to continue being oversupplied and price sentiment to remain weak.
The respective organisations listed in the above table