OSE Derivatives
Weather-Driven Volatility Reshapes the Global Rubber Market in 2024

Summary
- Weather events such as El Niño, coupled with macroeconomic challenges, shaped a complex landscape.
- Africa’s rubber production surged, while major Asian producers like Thailand and Indonesia saw declines.
- Weak demand, particularly in China, influenced inventory levels and price movements.
- Looking ahead, 2025 is expected to bring supply recovery but persistent challenges from bearish demand trends, policy uncertainties, and global economic factors.
- The EUDR implementation delay has added more volume to the physical market, and this, combined with the expectation of improved supplies in the second half of 2025, is expected to impact the pricing sentiment.
Weather Disruptions Dominate 2024
Following the heightened volatility in 2024 in the rubber market, the market participants are in a cautious frame, anticipating continued production disruption and an unpredictable demand scenario in 2025.
The El Niño phenomenon made 2024 the hottest year on record, significantly affecting rubber production cycles. In Thailand, unseasonal rainfall reduced tapping opportunities, with a shorter peak season predicted to lower early 2025 output. Helixtap forecasts a 10–15% decline in Thailand’s 2024 production.
Conversely, Africa has solidified its position as a critical player in the global rubber supply chain. Ivory Coast, in particular, contributed 1.7–1.8 million tons of rubber in 2024 (Helixtap Analitics, Customs Data), and Ghana is steadily enhancing its production capabilities. These developments position Africa as a counterbalance to supply disruptions in Asia, but the increasing reliance on African production raises questions about market diversification and sustainability.
Source: Malaysia Rubber Board (MRB), Helixtap calculations
Production Challenges in Southeast Asia
In recent months, due to unforeseen weather fluctuations, there has been a notable shift in market dynamics as production experienced a decline. Market sources predict a shorter peak this year than previously anticipated.
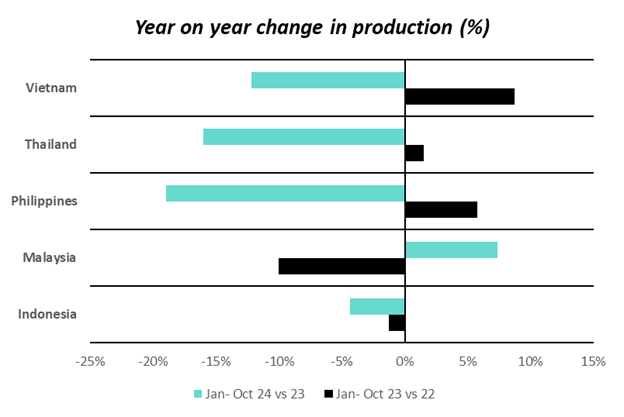
From January to October 2024, production levels among leading Asian rubber producing countries were noted to be lower compared to those in 2023. The producers in this context comprise Thailand, Indonesia, Vietnam, Malaysia, and the Philippines. According to the data available until October 2023, these countries experienced a decline in production over an extended period throughout 2023.
Improved weather conditions by Q4 helped alleviate some of these pressures, but year-end flooding in Thailand and Indonesia disrupted supply chains once again. In December of 2024, market participants across Thailand and Indonesia reported heavy rains affecting cup lump supply. According to the Thai Meteorological Station, the south of Thailand continued to have heavy rains that may cause flash floods and overflows in December.
The final quarter of the year typically coincides with the monsoon season in Southeast Asia. Specifically, in Thailand, this period is characterized by rainfall in the southern regions, including Hatyai, Yala, and Narathiwat. Usually, the upper South region experiences precipitation, but this year hasn’t shown this pattern.
Within the production group, in the first 10 months of the year, from January to October 2024, Thailand had the largest production decrease of about 699,000 tons, followed by Vietnam, which decreased by 138,000 tons, whilst Malaysian production grew by 21,000 tons as per MRB data. The remaining countries saw production contracting. As a result, the group production dropped 12% in the same period, which is expected to have a long-lasting impact on the supply situation. Even though the production is likely to improve next year, it is likely to cap a steep correction in the prices.
Malaysia and Thailand’s recent memorandum of understanding (MOU) to strengthen regional rubber trade may help mitigate future disruptions, but the full impact of these collaborations remains uncertain.
However, the market’s overall perception is that the supply is likely to ease over 2025, with expectations of more favorable weather compared to 2024.
Futures Market Highlights in 2024
1) Weak Demand and Inventory Pressure in China
The futures market mirrored the broader uncertainties in the rubber industry, with volatile trading across major exchanges.
On the macroeconomic front, China, the world’s largest rubber consumer, experienced an economic slowdown, with bearish demand trends persisting throughout the year.
Chinese inventories for TSR showed mixed trends in 2024. The physical rubber market was significantly influenced by high inventory levels, with economic indicators in China painting an unfavorable outlook. Additionally, the influx of low-cost warehouse cargoes has placed considerable downward pressure on market dynamics. Producer sources highlighted a substantial volume of African cargoes stored in Chinese warehouses, which could negatively impact the physical market. Meanwhile, some Chinese buyers are focusing on acquiring these warehouse cargoes, driven partly by the yuan’s prevailing weakness.
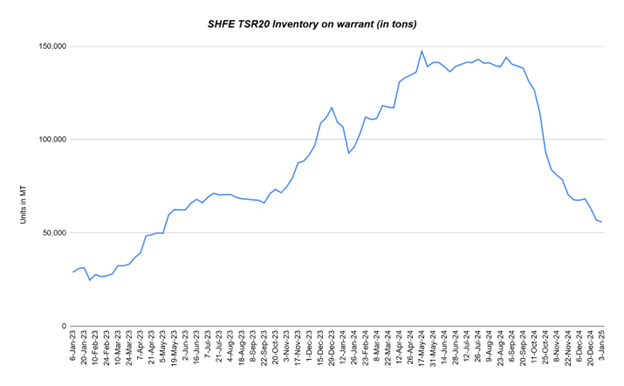
Looking at SHFE first, in 2024 there was a steady decline in the SHFE designated warehouse inventory levels on warrant since mid-October. Compared to the week of January 5, 2024, there has been a 37% decline in the inventory level as of December 13, 2024. The TSR inventory remains nearly twice as high as it was in early 2023, making immediate restocking unlikely.
TSR20 inventory levels in SHFE warehouses approached their highest in years, surpassing 100,000 tons since December 2023—a milestone last reached in April 2022. This suggests that domestic demand has remained subdued. However, stock levels have steadily declined since mid-October, with a 37% reduction recorded by December 13 compared to January 5. Despite this decrease, current inventories are still nearly double the levels seen in early 2023, reducing the likelihood of immediate restocking activity.
Nonetheless, China’s routine mid-year rotation of old reserve stocks is expected to trigger some restocking in 2025, according to market observers.
Source: SHFE & Helixtap
2) RSS3 Supply Shocks Linked to Thai Weather Conditions
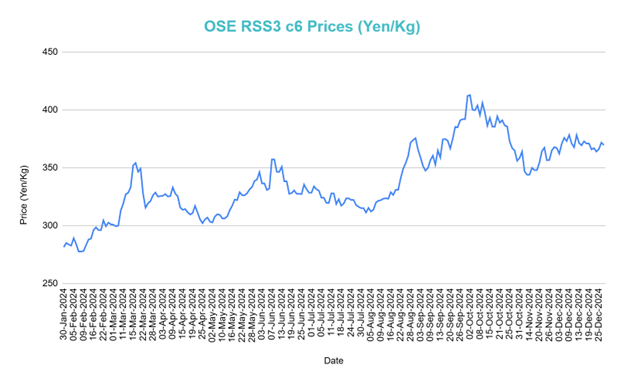
The Osaka Exchange (OSE) RSS3 futures contract is based on the underlying Thai RSS3 grade. Thus, movement on OSE RSS3 contract closely mirrored the tightness in supply and raw material amidst some flooding in major producer Thailand.
The chart shows OSE RSS3 c6 prices in 2024, starting near JPY300/kg and peaking above JPY400/kg in September after a strong bullish rally with higher highs and higher lows. The uptrend was confirmed by likely moving average crossovers early in the year.
Post-September, the market reversed sharply, showing a correction stabilizing around JPY370 /kg by year-end, where trading activities are typically muted. This level acts as key support, while JPY400 /kg remains a critical resistance for future movements.
The trend exhibits an initial bearish phase in 2022, driven by declining prices, followed by a sustained upward movement in 2023 and early 2024 before reversing in end 2024. The first major factors were market corrections or external shocks impacting supply-demand fundamentals. The second major factor that played a big role in price movements in 2024 was the USD/JPY currency fluctuations, which saw big movements and provided several arbitrage trading opportunities especially for mean reversion strategies.
Source: OSE
3) Global rubber futures sentiment ended weaker towards the end of the year
In the last few weeks of 2024 and first week of 2025, OSE RSS3, SHFE Natural Rubber and INE TSR as well as SICOM TSR20 futures similarly faced downward pressure. This price movement was due to a mix of factors, and include the rubber futures market reacting to China’s stock market dip along with some speculative selling due to weaker market sentiment and improved weather conditions in key production regions.
These developments underscore the continuous cautious sentiment that has pervaded the market towards the end of 2024 as traders return to the market and wait for more signals before re-entering the market.
Market Recap: Year in Review 2024 and Toward 2025
The timeline diagram below underscores significant macroeconomic influences shaping the market across 2023 and 2024, ranging from weather disruptions to geopolitical and economic events. Going into 2025, these factors will likely continue to impact rubber prices, but traders will need to shift focus toward demand signals, which were overshadowed in 2024 by unforeseen supply disruptions. Balancing these dynamics will be critical for navigating the market ahead.
Outlook for Rubber Market in 2025
2024 was focused on supply challenges, and whilst raw material prices of Thai cup lump are normalizing, demand factors and China market sentiment needs to come in before driving prices up.
1) Weather in Thailand – Look out for Wintering
With heavy rains in Thailand for a large part of the last quarter of 2024, there is some expectation of a shorter peak season. Additionally, the implementation of the EUDR is scheduled for December 2025, which could potentially lead to an increase in purchases during the second half of the year.
2) Demand signals – China and Globally
The primary obstacle for the market is the general negative outlook on demand. The delay in EUDR implementation has caused a lull in the physical market, and long–term contracts with tyre manufacturers have also experienced a similar sentiment.
Furthermore, China’s numerous stimulus measures are likely to have an impact on the Chinese economy, which, when combined with the recent decrease in inventory levels, could boost demand.
3) EUDR premiums from July 2025
The EUDR implementation delay has added more volume to the physical market, and this, combined with the expectation of improved supplies in the second half of 2025, is expected to impact the pricing sentiment. Several tyre manufacturers have delayed buying of EUDR grades in the first half of the year and this has had a negative impact to the premium levels for producers.
4) Tariffs and Macro Policies
Lastly, the tariff situation between the US and China is still unclear. While some market observers believe China might opt to ease the yuan to buffer any tariff impact, there is still uncertainty until Donald Trump’s inauguration ceremony.