OSE Derivatives
Rubber Market Fundamentals: Navigating Uncertainty Amid EUDR Implementation and Global Supply Constraints

The global rubber market is currently characterized by a complex mix of factors that are contributing to significant uncertainty. Key among these factors is the impending implementation of the European Union Deforestation Regulation (EUDR), which continues to spark debate and negotiation. On top of regulatory pressures, the market is also grappling with supply-side disruptions, volatile demand forecasts, and weather-related challenges. Together, these elements make the present landscape of the rubber market at an interesting turning point.
EUDR Implementation: A Looming Challenge with a Temporary Reprieve
The European Commission’s proposal to extend the EUDR phasing-in period by an additional 12 months has reignited discussions about its impact on the global rubber supply chain. In October 2024, EU member states officially backed the 12-month delay[1], providing businesses and exporting countries more time to prepare for compliance with the regulation. The decision was made during a meeting of ambassadors from the 27 EU member states in Brussels, marking a significant development in the regulation’s timeline. However, the delay still requires formal approval from the European Parliament, expected this month.
The EUDR is designed to combat deforestation linked to the production of key commodities, including rubber, cocoa, coffee, soy, and beef. Although the delay has been welcomed by some stakeholders, the broader market sentiment suggests that while the postponement offers temporary relief, the regulation will ultimately transfer the supply chain in profound ways. For rubber, the industry pulled together and made great efforts to prepare ahead of time.
The EUDR stipulates that importers must track the origins of their commodities, ensuring that the products do not come from deforested regions after 2020. Implementing such intricate tracking systems poses logistical challenges and may increase operational costs for businesses, adding further pressure to the market. For rubber producers and buyers alike, the delay could offer short-term relief, but it also prolongs the uncertainty that has clouded market decisions.
However, looking at fundamentals this year, there were pockets of increased spot demand due to weather inclement factors (RSS3 domestic supply in India as well as flooding in many parts of Thailand).
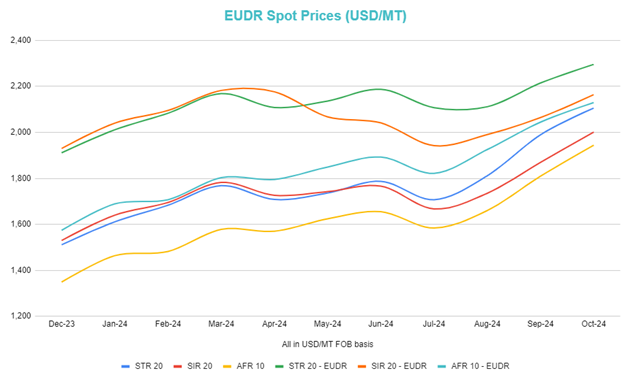
In the chart below, we plot the various grades EUDR spot prices for the period of Dec 2023 till Oct 2024. Whilst these are for TSR20 physical spot grades, they represent the premiums and are a good gauge on how the market is trading it, and a similar sentiment would likely be observed across various grades. Overall, we can see that the premiums started to stabilize and increase since May 2024 and whilst the sharp increase has evened out, due to the likely delay of the EUDR implementation, this dip may be short term if the supply continues to face constraints.
Source: Helixtap Assessments
Market Response to Regulatory Pressures
The prospect of EUDR implementation has already led to shifts in the market. Some tire manufacturers have delayed their purchases of rubber especially for cargoes loading further out in January 2025.
The correction in EUDR premiums further indicates that market participants are adjusting their expectations ahead of the legislation’s rollout.
Despite the challenges, many industry insiders believe that the EUDR will eventually be implemented, although potentially with renegotiated premiums. Both buyers and sellers have invested time and money in preparing for compliance, and it seems unlikely that the regulation will be scrapped altogether. However, the evolving demand dynamics—marked by a weakening global economic outlook and changing consumption patterns—add further complexity to the situation.
Price Movements: Tight Supply was a major factor this year
Rubber prices have been on a bullish trajectory throughout much of 2024, driven by tight supply conditions and the ripple effects of adverse weather. Prices surged in the first half of the year due to early wintering and supply-chain constraints took their toll. The market has responded to these pressures with a series of corrections, but prices remain elevated compared to previous years.
The volatility in rubber prices is further exacerbated by the uncertainty surrounding the EUDR. Any delay in the regulation’s implementation could provide temporary relief for buyers, as it may ease the upward pressure on prices. However, the long-term outlook remains highly uncertain, with both supply and demand factors poised to play significant roles in determining future price movements.
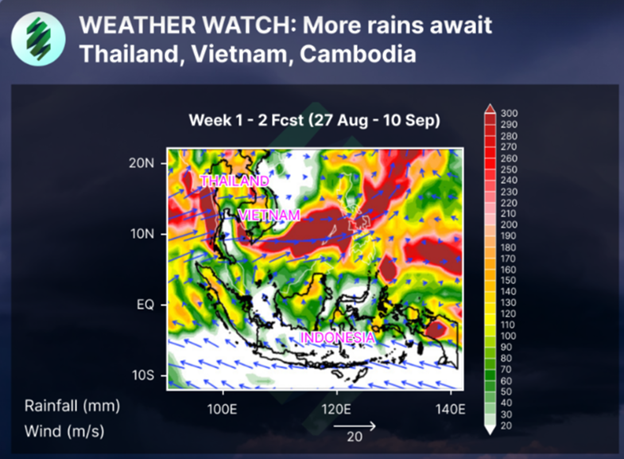
In the diagram below, it highlights the weather conditions in August and September when the OSE RSS3 futures and physical prices experienced sharp rises which brought about very heavy rain and there was a shift taking place from ENSO neutral condition to La Nina which led to more rains in the region than normal.
Source: Helixtap
While regulatory issues dominate much of the conversation, supply-side constraints are also playing a pivotal role in shaping market conditions. Rubber production has been significantly impacted by adverse weather events this year. In Southeast Asia, the onset of El Niño has disrupted tapping activities, leading to lower-than-expected output. In regions like the Ivory Coast, heavy rainfall has compounded these issues, contributing to tight supply conditions in the short term.
How will this play out in the futures market?
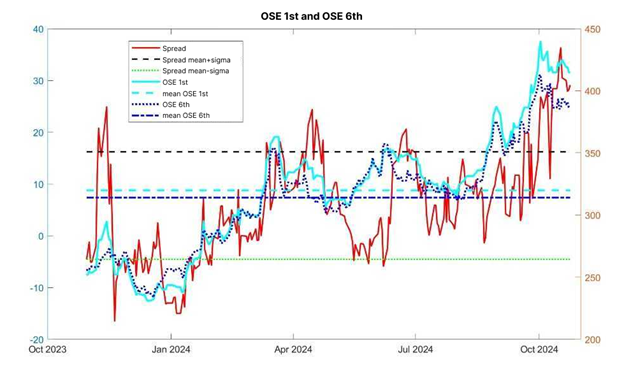
In the chart below, we analyze the OSE 1st and 6th position and look to see where the mean levels are. The right axis shows the futures price (Yen/Kg), and the left axis shows the spread between 6th and 1st position. In September and October 2024 further steep spikes were observed reaching multi year highs and the differential was about 100 Yen/Kg from the mean of the last year. As this spike was largely driven by supply factors affecting the largest producer Thailand, generally better weather conditions could be a factor to move prices downwards towards the 300 Yen/Kg range.
Furthermore, looking at Japan OSE rubber stocks, data from 20 October 2024 shows 2,437 MT, a decrease in 125MT week on week. This similar trend of lower inventory week on week is also observed in Shanghai SHFE rubber stocks. This is one of the historical lows due to the supply disruptions in Thailand and higher spot prices observed this year. Inventory is a good proxy for demand conditions and something which traders can monitor for any signs of restocking for instance.
Source: OSE
Demand Outlook: A Major Factor to sustain further uptrends
On the demand side, there are some headwinds. Weak growth in global rubber demand, particularly in the automotive sector, has emerged as a key concern for market participants. The automotive industry is a major consumer of rubber, with tire production alone accounting for nearly 70% of global rubber consumption[2] . As such, any shifts in vehicle production or demand have a pronounced effect on rubber markets.
The rise of Chinese electric vehicles (EVs) is another factor contributing to the evolving demand landscape. China, which accounted for 60% of global EV sales in the first half of 2024, has emerged as a dominant player in the sector[3]. This growth has implications for the European Union, where there is a battle for market share.
The market’s primary concern is the potential for a prolonged period of weak demand growth, especially as macroeconomic conditions remain uncertain. Inflationary pressures, geopolitical tensions, and fluctuating commodity prices all contribute to a challenging environment for forecasting future demand.
Conclusion: A Market in Flux could provide arbitrage opportunities
As the market continues to navigate these challenges, both producers and buyers will need to remain adaptable. This would include monitoring the futures positions and spotting trading opportunities when there are big dislocations.
The OSE RSS3 futures market is closely linked to the Thai RSS3 grades and any supply constraints would be major factors to watch out for trading opportunities. Separately, earlier this year, flooding in Kerala in August[4], saw Indian domestic RSS4 grades impacted. Thus, many Indian tyre manufacturers had to rely on imported RSS grades from Thailand. Whilst this has tided through, any changes in Indian domestic supply would have an indirect impact in Thai RSS3 demand, and naturally also the OSE RSS3 futures.
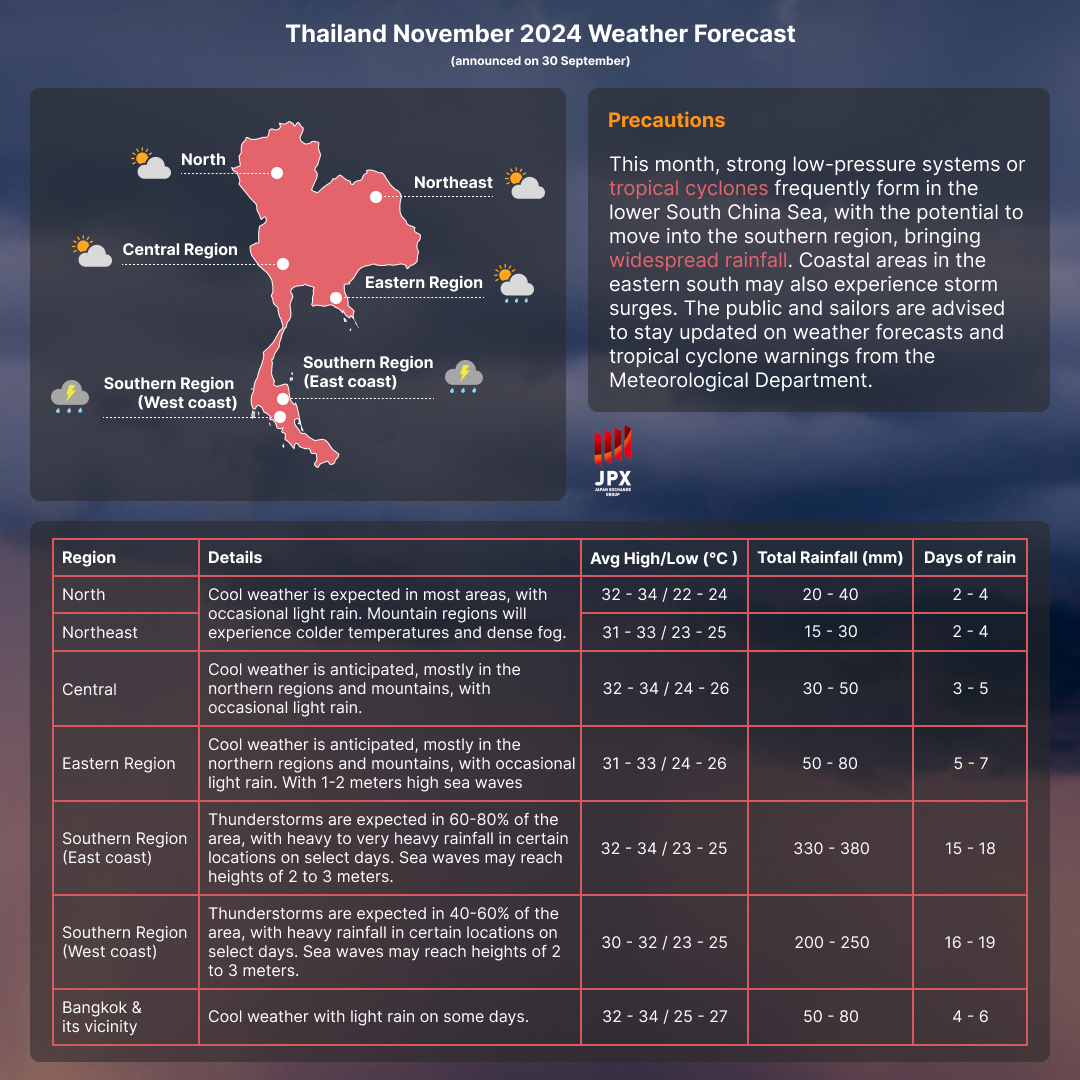
Looking at the November 2024 forecast according to the Thai Meteorological Department, the Southern regions may be impacted by wet weather and is something traders should look out for and monitor.
Source: Thai Meteorological Department
[1] European Commission Press Release
[2] Us Tire Manufacturers Association (USTMA)
[3] IEA Global Electric Vehicle (EV) Outlook 2024 Report
[4] BBC article, 2 Aug 2024 “Search for Bodies after India Landslide buried hundreds”